Introduction
In presenting the 2023-24 Union Government Budget, the Finance Minister stated that this is the first year of India’s Amrit Kaal, the 25-year period ending in 2047 when India will complete 100 years of independence. In the Amrit Kaal period, when the global and domestic environment will be uncertain, volatile, and complex, with many known as well as unknown unknowns, India will need to manage its rise.
PM Modi has articulated that the main purpose of ‘Amrit Kaal’ is to reduce economic disparities among the citizens of India, emancipate people residing in villages, make India more technically agile, and reduce dependence on the government. “While India has made rapid strides, there should be a ‘saturation’ of development and 100 percent accomplishments with every village having roads, every family having a bank account, every eligible person having
health insurance, card, and gas connection” .
In Amrit Kaal India wants to strongly underline that Democracy can deliver broad-based growth on a sustained basis, with sustainable robust social safety nets. The other big shift is reordering the Indian economy and recasting the global perception about it under Modi—wherein India is now seen as part of the solution and not part of the problem. Whether it is climate change—committing India to net zero carbon emissions in 2070—or promoting trade through striking Free Trade Agreements (FTA) with the United Arab Emirates, and Australia and working on similar deals with England and the United States—India is increasingly contributing to global decision making. Its leadership of the G20 countries only lends it a greater opportunity to grow this perception. During its Presidency, India is bringing the concerns of the Global South to the mainstream of global discussions.
Indian diplomacy has responded in the last decade by :
1. Practicing non-reciprocal relationships with our proximate neighbors through the Neighborhood First policy.
2. Having a positive approach towards our extended neighborhood with Act East, Link West, Central Asia & SAGAR policies. As part of SAGAR (Security and Growth for All in the Region), the Indian government, the Indian Navy, and the Indian Coast Guard have assisted countries in the Indian Ocean region with exclusive economic zone
surveillance, search and rescue, and other such activities, including first responder initiatives.
3. Engaging major nations and groupings without constraining our options.
4. .Strengthening our solidarity with Global South by voicing their concerns.
5. Planning for an era ahead where we will move to be a leading power and beyond. EAM Dr S. Jaishankar.
Performance of Select Indicators between 2014-22 and Prospects
• The next slide presents India’s progress between 2014 and 2022 in selected indicators.
• Note that continuing progress in these and other economic and social indicators would be a crucial component of achieving growth, and enhancing sustainability and resilience in the Amrit Kaal.
Performance of Select Indicators between 2014-22 and Prospects India aims to be the third-largest economy in the world well before the end of Amrit Kaal in 2047
• Real GDP in India has surged by 355% over the last twenty-six years contributing almost 15% of global output growth since 2012. This has pushed India’s share of the world output up to close to 10% making it the third-largest economy by size. In the last ten years, the country’s cumulative annual average real growth rate has been 5.5%.
• GDP in Purchasing Power Parity terms with added estimates for the size of the informal economy and adjustments for out-of-date GDP base year data.
J. Morgan has estimated that about one-fifth of global growth in the next 20 years will be contributed by India, whereas its share in Global nominal GDP is less than four percent.
• A significant contribution by India to global growth also implies a similar contribution to global trade.
• India is expected to end the fiscal year 2022-23 with a total of US$760-770 billion worth of exports of merchandise and services, with the former exhibiting a high deficit, and the latter a substantial surplus.
• India’s Foreign Trade Policy (FTP) 2023 has no time period, and it is open to consultative feedback with a target of USD 2 trillion in exports by 2030. AS India traditionally has a trade deficit, imports are likely to exceed USD 2 trillion by 2030, giving opportunities to global firms to access the global market.
It envisages substantial process reforms such as
-Online approvals without physical interface
-E-certificate of origin issuance
-Paperless filing
-Consultative mechanism to be introduced to resolve trade and industry grievances and concerns
New export hubs have been announced as well as measures targeting e-commerce, dairy, and apparel and clothing sectors, among others.
The new FTP also seeks the internationalization of domestic currency and will facilitate global trade payments in rupees.
• India’s household income composition (next two slides) that during the Amrit Kaal India will increasingly become middle class, requiring concomitant mind-set and public policy change away from the notion that India is poor.
• India’s tremendous achievement is to nearly end extreme poverty.
• Long experience suggests that Policies made in the name of the poor are poor policies.
• In Amrit Kaal public policies will need to be geared towards aspirations and concerns of the middle class who will form majority. And also will be urban.
• Another change needed therefore is to think of India as majority urban or para-urban and not excessively focus on rural populations.
• Both these change would contribute to growth and resilience as well as sustainability.
• India’s progress towards a middle-class nation, will also be accompanied by good livelihood prospects and improve ease of living as connectivity, physical and digital, and other measures empower persons, especially women.
• In addition schemes such as the Pradhan Mantri Mudra Yojana (PMMY) has enabled more than 350 million beneficiaries to obtain collateral-free loans worth INR 19.22 trillion since 2015 when the scheme began.
• ”Majority of India’s care work is informal, non-marketable activity, & not valued.
India has 120 million people above the age of 60. We are a fast-aging country & women are at the heart of providing care work,” Shamika Ravi Member, Economic Advisory Council to Prime Minister.
India’s Initiatives for the Amrit Kaal for Growth, Resilience, and Sustainability
India’s Chief Economic Advisor, Dr Anantha Nageswaran, has suggested the following general guideline to deal with uncertainty, which is likely to be a key characteristic of the global and domestic environment in the Amrit Kaal.
India – A Reformed Agenda for 2047
Sanjeev Sanyal
He emphasizes India pursuing a supply-side strategy, with an emphasis on risk-taking and creative destruction, with adequate social safety nets (not entitlements), with due emphasis on the provision of essential goods and services; and the use of technology. India already has had encouraging results using technology to deliver serves, and to transfer benefits directly to the bank accounts of the beneficiaries. The JAM (Jan Dhan, Aadhar, and Mobile) combination has enabled India to be a world leader in on-line payments, with UPI (United Payments Interface) increasingly spreading abroad as well.
UPI is an instant real-time payment system developed by the NPCI. It facilitates three types of transactions: P2P (Peer to Peer), P2M (Person to Merchant), and P2PM (for small merchants and the unorganized retail sector).
India has “700 million smartphone users, who…consume an average of almost 17 GB in mobile
data per day, higher than the 13 GB in China and the 15 GB in North America.“’
And at significantly cheaper prices. India contributed only 4 percent to cumulative carbon emissions between 1850 and 2019. In absolute terms, it is the third largest emitter, but its per capita remain low, but expected to increase as its per capita income and its GDP increase. It is in India’s interest to integrate environmental sustainability as ONE of the goals during Amrit Kaal and beyond. This goal needs to be balanced with other goals. Facilitating a circular economy is one of the approaches to balance environmental goals with other goals.
India is quietly building a naval base in the Great Nicobar Island overlooking the #Mallaca Straits & 90 miles from the “tip of Indonesia”, writes Admiral Raja Menon (retd). This could transform the balance of power in the arc from the South China Sea to the Indian Ocean.
India needs to increase deep ports to match its rising international trade.
The Circular Economy A Perspective from Korea
Rajeev Mantri Twitter March 30, 2023
How exactly does Gati Shakti inform and enhance infrastructure development? By using the latest spatial imaging technology, provided by start-ups like @Aereo_NextisNow, project planning, implementation, and monitoring are all dramatically improved.
Rajeev Mantri Twitter March 30, 2023
• The Indian Army will be hosting the first-ever India-Africa Chiefs Conclave in Pune on March 28. As part of its outreach to African nations, the conclave will be attended by Army chiefs from 25 African countries. The event will focus on enhancing peace and security between India and Africa and creating opportunities for exchanging ideas
and perspectives. The Indian Defence Ministry, Foreign Ministry, and Service HQs will participate in the conclave.
• The conclave will take place in two sessions, where the first session will focus on exploring the key pillars of the India-Africa Defence Partnership, and the second session will focus on the Indian Defence Industry’s Outreach to Africa. –India and African armies to conduct AFINDEX next week
• Seven to eight countries are expected to sign up for and implement ‘India Stack’ at the India Stack Global Conference in May 2023.
• ‘India Stack’ is the moniker for a set of open APIs and digital public goods that aim to unlock the economic primitives of identity, data, and payments at the population scale.
• The project represents a collection of disparate technology products and frameworks.
• The components of this collection are owned and maintained by different Indian agencies.
• The principles, technologies, and functionality of India Stack can be applied in any country, whether it’s developed or emerging.
• None of the systems which comprise India Stack require any proprietary technology or intellectual property that would preclude their implementation in any country.
• At its core, the driving vision of India Stack is of open networks those that enable the setting up of a level-playing field for members of a digital ecosystem to enable application developers to focus on building the best consumer experiences and products instead of having to worry about infrastructure, permissions, and access.
The government launched the Open Network for Digital Commerce (ONDC) last year to enable small merchants and local stores across the country to access processes and technologies typically deployed by large e-commerce platforms like Amazon and Walmart. ONDC is in talks with more companies in the sector across several cities to bring them on board over the next few months.
Union Minister of Ports, Shipping and Waterways (MoPSW) Sarbananda SonowaI has said India aims at becoming a ‘Global Hub for Green Ship’ building by 2030 with the launch of the Green Tug Transition Programme (GTTP).
Inaugurating India’s first National Centre of Excellence in Green Port and Shipping (NCoEGPS) in Haryana’s Gurugram on Wednesday (22 March 2023), Sonowal said the program will start with ‘Green Hybrid Tugs’, which will be powered by green hybrid propulsion systems, and subsequently adopting non-fossil fuel solutions like (methanol,
ammonia, hydrogen).
India must lead in 6G technology: Union IT and Telecom Minister Ashwini Vaishnaw. More than 127 patents for 6G technologies have been obtained by India.
On Friday, 31 March 2023, the central government notified the India International Arbitration Centre (Criteria for admission to the panel of arbitrators) Regulations, 2023.
The Chamber of Arbitration, which will consist of experienced and reputable arbitration practitioners at the national and international levels, will empanel arbitrators for a maximum period of five years.
The chamber will appoint its members for two years, with a provision for re-appointment.
Persons proficient and willing to serve as arbitrators for either domestic or international arbitration or both, subject to their expertise and experience, will be empanelled by the chamber.
One more step in Constructing International Financial Centre in India
• In order to better understand the nuances from regulatory, tax, legal, and other perspectives and identify measures required to make India (GIFT IFSC) the preferred location, IFSCA has constituted an expert committee to formulate a roadmap to onshore the Indian innovation to GIFT IFSC.
• This committee will be chaired by Shri G. Padmanabhan, former Executive Director, of the Reserve Bank of India. The committee includes representatives from leading Venture Capital funds, Start-ups, FinTech’s, Law firms, Tax firms, and other domain experts.
• The Indian start-up ecosystem is the third largest start-up ecosystem in the world, boasting an impressive 115 unicorns (billion-dollar enterprises). Indian start-ups raised $44 billion in 2021, with over $ 33 billion going towards deals worth more than $5 million. Many Indian start-ups are domiciled outside India – despite having the majority of their market, personnel, and founders in India. These “externalized” or “flipped” start-ups constitute a large number of India’s unicorns.
• The terms of reference for the committee include measures required to encourage the Indian Fintech / Start-ups domiciled abroad to relocate to GIFT IFSC. Further, the committee would also identify issues that are critical to the development of GIFT IFSC as a global Fintech Hub, besides suggesting measures to encourage new FinTech’s to have a global outlook to set up their commercial presence in GIFT IFSC. Additionally, the committee would also identify challenges and recommend measures for the development of the International Innovation Hub at GIFT IFSC. The committee is expected to submit its recommendations to IFSCA within three months.
India’s RBI gives go-ahead for trading in national currencies for 18 countries: Tanzania, Kenya, Uganda, Botswana, Fiji, Germany, Guyana, Israel, Malaysia, Mauritius, Myanmar, New Zealand, Oman, Russia, Seychelles Singapore, Sri Lanka, United Kingdom
• The Ayushman Bharat, also known as the Pradhan Mantri Jan Arogya Yojana (PMJAY), covers the bottom 40 percent of the population.
• Ayushman Bharat scheme (2018) offers up to Rs 5 lakh coverage for secondary and tertiary healthcare to underprivileged people.
• An Ayushman Bharat 2.0 is in the works, with the objective to cover the 400 million citizens in the middle-income bracket.
• This would be in addition to the 500 million citizens already covered under the same scheme.
• The total insured would then be 900 million citizens or close to 75 percent of India’s population.
• With over 500 million beneficiaries today, and perhaps close to 900 million in the future, the policy will produce data that will require elaborate expertise to be transformed into meaningful knowledge.
• By doing so, India will be able to go from a reactive healthcare model to a preventive healthcare model.
Select Public Policy Challenges
Among the major public policy challenges in the Amrit Kaal are:
1. Demographic Challenges.
2. Better public financial management in the states and in urban and rural bodies.
3. Indian corporates need to spend more on R and D.
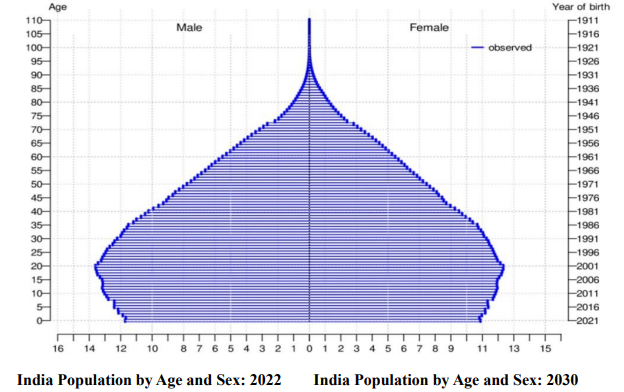
India will also need to adjust to falling global fertility trends and the implications of wide variations in fertility rates worldwide.
Select Public Policy Challenges
Over 30 yrs., pension payment as % of development expenditure reveals: 1) NPS was major breather to ALL states 2) Some states have managed to keep burden low: GJ, HR, MH, KA, MP, CT (< avg. for all states: red line) 2) Some states reeling under pressure: TN, KL, PB.
Interesting data on R&D as a percentage of India’s consolidated industry sales and profits. India
lags quite a bit. This needs to be corrected if we need to accelerate growth.
Using India’s languages more strategically to gain ECONOMIC AND SOFT-POWER advantage
Concluding Remarks
•India is pursuing many diverse policies and taking numerous initiatives to help progress towards the goal of Amrit kaal as evidenced by the selected examples given in this presentation.
• Changing nature of globalization, from lowest price sourcing to ‘friend shoring’, and where trust, reliability, and common values and interests are what defines ‘cheapness’ makes a challenging environment.
•This requires focus, confidence in India’s civilization, values,, and leadership, and desire by all stakeholders to take the opportunity to become a global power.
•India is working for solutions to global challenges: establishing resilient supply chains; dealing with the digital era; preparing for a global workplace and addressing deficits in global commons.
•In solutions to these and more, the power of India’s example will have a role. Also, as a civilizational state, showcasing India’s culture and heritage is a priority.
•A sharper awareness of Comprehensive National Power needs to factor in the importance of technology, the building of deeper strengths at home and prepare for a global footprint.
•The world of academia and research institutions have a special responsibility in contributing to India’s rise during the Amrit Kaal.









